Leveraging Data Storage and Databases on Google Cloud Platform
Leveraging data storage and databases on Google Cloud Platform (GCP) can greatly enhance your applications’ scalability, performance and reliability.
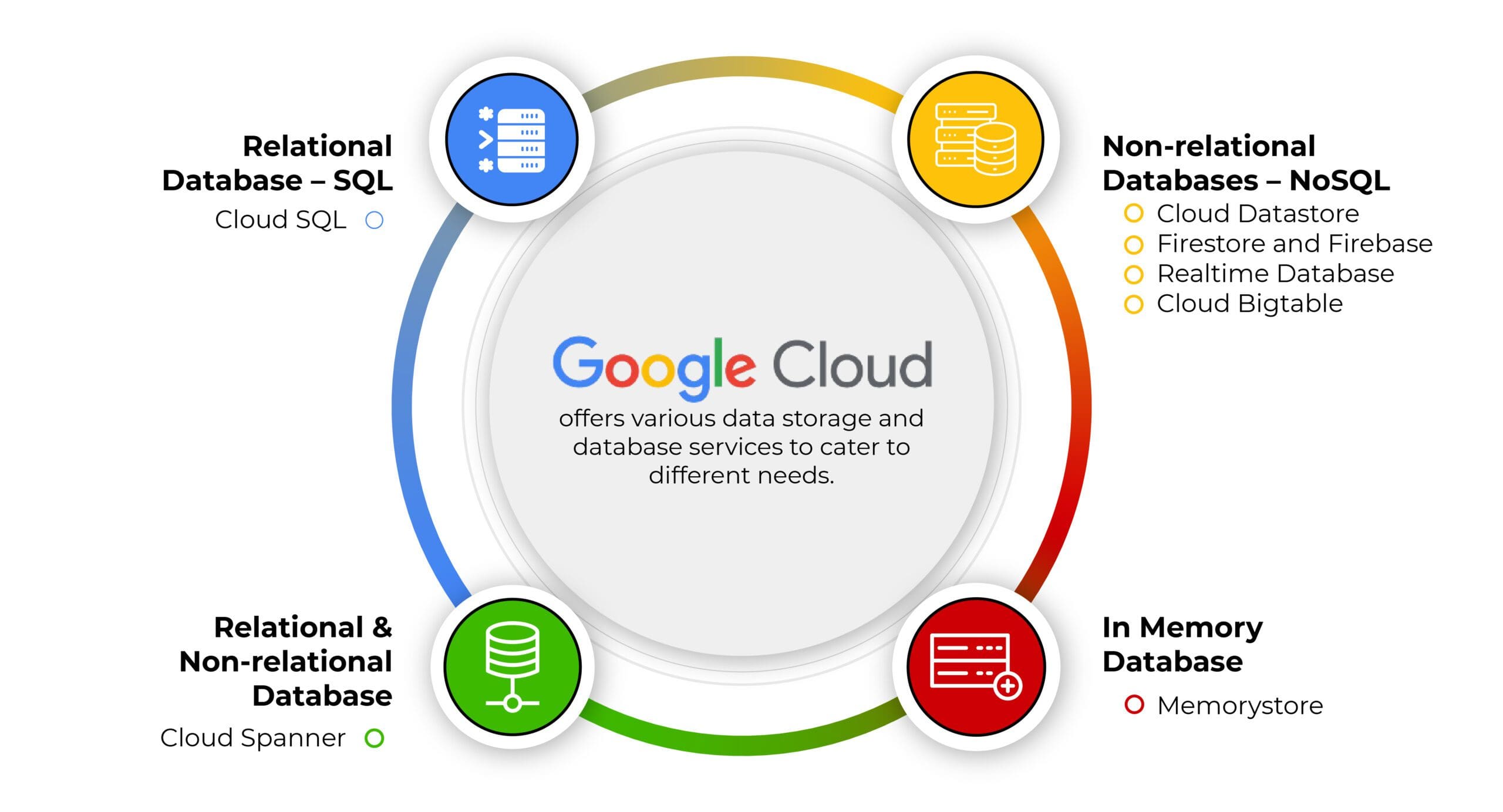
Google Cloud offers various data storage and database services to cater to different needs.
Here are some key services and concepts to consider when leveraging data storage and databases on GCP:
Cloud Storage
Cloud storage refers to the practice of storing digital data, such as files, documents, photos, and videos, on remote servers accessed through the internet. Cloud storage offers a scalable and flexible solution for individuals and businesses to manage and share their data securely across different platforms.
Google Cloud Storage is an object storage service that allows you to store and retrieve any amount of data securely. Object storage is a data storage architecture for storing unstructured data, which sections data into units—objects—and stores them in a structurally flat data environment. Each object includes the data, metadata, and a unique identifier that applications can use for easy access and retrieval.
You can use Cloud Storage for both application data and static assets. Cloud storage can also be used to store long term data or backups for compliance purposes at a very low cost.
Database Services
Google Cloud Platform offers a comprehensive range of managed database services, including Cloud SQL for relational databases, Cloud Firestore and Cloud Bigtable for NoSQL databases, and Cloud Spanner for globally distributed, horizontally scalable, and strongly consistent data storage.
Choosing between a relational and non-relational database depends on how your data is organised and the needs of your application. If your data structure will stay mostly the same, go for a relational database like Cloud SQL. If you need a large, consistent, and scalable database, consider Cloud Spanner. If your data structure might change in the future and you need high scalability and availability, a non-relational database is a good choice.
Let’s take a look at Google Cloud Platform’s offerings in more detail.
Relational Database – SQL
-
Cloud SQL
Cloud SQL is a fully-managed relational database service that supports popular database engines like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQL Server. A relational database is a collection of data items with pre-defined relationships between them.
It handles database management tasks like backups, network connectivity, logging, patches and updates, so you don’t have to build and maintain them yourself, allowing you to focus on application development. It’s a good choice if you need a traditional SQL database.
Cloud SQL is like a traditional database where data is organised in tables with fixed rules. It’s great for applications with structured data and complex operations, but scaling can be limited. On the other hand, NoSQL databases are more flexible and can handle various types of data, even if it’s not neatly organised. They scale easily to manage huge amounts of data, making them ideal for big data and real-time applications. Google Cloud Platform caters to both.
Best for CRM, enterprise resource planning (ERP), eCommerce and web, and SaaS applications.
Relational & Non-relational Database
-
Cloud Spanner
Cloud Spanner is well-suited for applications that need a globally distributed database with strong consistency and high scalability. It’s designed for applications in various industries, including finance, e-commerce, gaming, and more, where low-latency, highly available, and strongly consistent data storage is critical for the success of the application.
It is a no-compromise database that gives you high performance and availability at virtually unlimited scale. A “no-compromise database” refers to a database system that excels in all essential aspects without requiring any trade-offs or compromises in its performance, features, scalability, reliability and ease of use.
A no-compromise database is also reliable and robust, ensuring data durability and availability, even in the event of hardware failures or network issues. It provides automated backup and recovery mechanisms, safeguarding your data against unexpected losses.
Best for gaming, retail, global financial ledger, and supply chain or inventory management.
Non-relational Databases – NoSQL
-
Cloud Datastore
Cloud Datastore is a highly scalable non-relational database or NoSQL database for your web and mobile applications.
A non-relational database is a type of database that stores and manages data without requiring a fixed schema, allowing for flexible and scalable data storage.
Cloud Datastore provides a flexible and scalable NoSQL database solution for applications that need structured and semi-structured data storage with automatic scaling capabilities. It’s a good option for smaller applications and prototyping. It offers automatic scaling and high availability, making it suitable for web and mobile applications handling varying workloads and data types.
The next generation of Datastore is Firestore.
-
Firestore and Firebase Realtime Database
Firestore and Firebase Realtime Database are part of Firebase, Google’s mobile development platform that empowers you to quickly build and grow your apps. Firestore is a NoSQL document database that is part of Firebase, while Firebase Realtime Database is a real-time JSON database, a comprehensive app development platform from Google. Both are suitable for building real-time applications and sync data across devices.
Firebase and Google Cloud share three products: Firestore, Cloud Functions, and Cloud Storage. Firebase is a BaaS platform (Backend-as-a-Service) offering a wide variety of features and components for enhanced mobile and web application development. It is preferred by many business owners and developers due to the level of usability it offers.
Best for mobile/web/IoT applications, real-time sync, and offline sync.
-
Cloud Bigtable
Google Cloud Bigtable is a scalable, NoSQL database service optimised for large analytical and operational workloads. It’s a good fit for time-series data, IoT data, and other applications that require low-latency access to large datasets.
Bigtable is a special type of database that can store enormous amounts of data in a way that allows for very quick access. It is great for handling different kinds of data, like organised information, partially organised data, or even data without a specific structure. Bigtable is super fast when it comes to reading and writing this data. Many important Google services like YouTube, Google Analytics, Search, Ads, Drive, and Maps use Bigtable to make sure they work smoothly and efficiently.
It has single-digit millisecond latency, limitless scale, and 99.999% availability for large analytical and operational workloads.
Best for personalisation, adtech, recommendation engines, and fraud detection.
In Memory Database
-
Memorystore
Reduce latency with scalable, secure, and highly available in-memory service for open-source Redis and Memcached. Google Cloud Memorystore is a fully managed, in-memory data store service that is 100% compatible with Redis and Memcached. It provides a caching solution that allows users to store and retrieve data in RAM, offering extremely fast read and write access times. Memorystore is used for caching frequently accessed data to improve application performance and reduce the load on primary databases.
Memorystore automates complex tasks for Redis and Memcached such as enabling high availability, failover, patching and monitoring so you can spend more time coding. Choose the right engine that fits your cost and availability requirements.
Best for caching, gaming, leaderboard, and social chat or news feeds.
Best Practices
Here are a few best practice suggestions to consider when leveraging data storage and databases on Google Cloud Platform:
- Data Security: Utilise encryption at rest and in transit to ensure the security of your data. Google Cloud provides built-in features to help you encrypt your data effectively.
- Data Backup and Disaster Recovery: Set up regular backups and implement disaster recovery strategies to prevent data loss and ensure business continuity.
- Scaling: Choose the appropriate data storage or database service based on your application’s requirements and expected growth. Google Cloud services are designed to scale, so ensure your architecture can handle increased demand.
- Monitoring and Logging: Implement monitoring and logging to track the performance and health of your data storage and databases. Google Cloud’s operations suite provides useful tools for this purpose.
- Access Control: Define proper access controls and roles to ensure that only authorised users have access to your data and databases.
- Cost Optimisation: Optimise your data storage costs by selecting the appropriate storage class in Cloud Storage or provisioning the right instance size for your databases.
By carefully selecting and using the appropriate data storage and database services on Google Cloud Platform, you can build robust, scalable, and efficient applications that meet your business needs.
Chat with the team at Radical Cloud Solutions if you are interested in upgrading your infrastructure and moving to Google Cloud Platform.